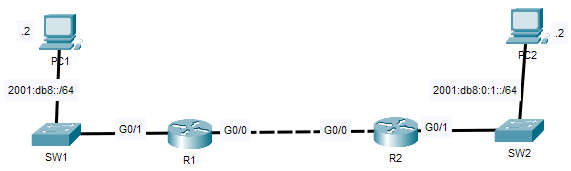
Use EUI-64 to configure IPv6 addresses on G0/1 of R1/R2
Configure the appropriate IPv6 addresses/default gateways on PC1 and PC2.
Enable IPv6 on G0/0 of R1/R2 without explicitly configuring an IPv6 address.
Configure static routes on R1/R2 to enable PC1 to ping PC2.
Router 1 Configuration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 R1>en R1# R1#show int g0/1 GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected) Hardware is CN Gigabit Ethernet, address is 0030.f236.4502 (bia 0030.f236.4502) Internet address is 10.0.1.254/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit, DLY 10 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Full-duplex, 100Mb/s, media type is RJ45 output flow-control is unsupported, input flow-control is unsupported ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00, Last input 00:00:08, output 00:00:05, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/75/0 (size/max/drops); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue :0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort 0 watchdog, 1017 multicast, 0 pause input 0 input packets with dribble condition detected 0 packets output, 0 bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 0 collisions, 1 interface resets R1# R1# R1#
R1 G0/1 interface is shown in the command above.
MAC: 0030.f236.4502
Step 1: 0030.f2 36.4502
Combine the network prefix 2001:db8::/64 with the EUI-64 interface ID.
2001:db8::0230.f2ff.fe36.4502/64
Now to configure the interface automatically.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 R1#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)# R1(config)#ipv6 uni R1(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing R1(config)# R1(config)#int g0/1 R1(config-if)# R1(config-if)#ipv6 ? address Configure IPv6 address on interface authentication authentication subcommands dhcp IPv6 DHCP interface subcommands eigrp Configure EIGRP IPv6 on interface enable Enable IPv6 on interface flow NetFlow Related commands hello-interval Configures IP-EIGRP hello interval mtu Set IPv6 Maximum Transmission Unit nat Enable IPv6 NAT on interface nd IPv6 interface Neighbor Discovery subcommands ospf OSPF interface commands rip Configure RIP routing protocol summary-address Summary prefix traffic-filter Access control list for packets unnumbered Preferred interface for source address selection R1(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8::/64 ? anycast Configure as an anycast eui-64 Use eui-64 interface identifier <cr> R1(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8::/64 eui-64 R1(config-if)# R1(config-if)#do sh ipv6 int brief GigabitEthernet0/0 [up/up] unassigned GigabitEthernet0/1 [up/up] FE80::230:F2FF:FE36:4502 2001:DB8::230:F2FF:FE36:4502 GigabitEthernet0/2 [administratively down/down] unassigned Vlan1 [administratively down/down] unassigned R1(config-if)#
On top of the generated ipv6, notice a link-local address FE80::230:F2FF:FE36:4502, FE80 network prefix is link-local.
R2 Configuration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 R2>en R2#show int g0/1 GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected) Hardware is CN Gigabit Ethernet, address is 0001.63b0.b802 (bia 0001.63b0.b802) Internet address is 10.0.2.254/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit, DLY 10 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Full-duplex, 100Mb/s, media type is RJ45 output flow-control is unsupported, input flow-control is unsupported ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00, Last input 00:00:08, output 00:00:05, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/75/0 (size/max/drops); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue :0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort 0 watchdog, 1017 multicast, 0 pause input 0 input packets with dribble condition detected
Manually determine the EUI-64
MAC: 0001.63b0.b802
Step 1: 0001.63 b0.b802
The diagram shows the ipv6 prefix to be: 2001:db8:0:1
2001:db8:0:1::0201.63ff feb0.b802/64
Now let’s confirm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 R2# R2#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R2(config)# R2(config)#ipv6 uni R2(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing R2(config)# R2(config)# R2(config)#int g0/1 R2(config-if)# R2(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8:0:1 eui-64 ^ % Invalid input detected at '^' marker. R2(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8:0:1/64 eui-64 ^ % Invalid input detected at '^' marker. R2(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8:0:1::/64 eui-64 R2(config-if)# R2(config-if)#do show ipv6 int g0/1 brief show ipv6 int g0/1 brief ^ % Invalid input detected at '^' marker. R2(config-if)#do show ipv6 int brief GigabitEthernet0/0 [up/up] unassigned GigabitEthernet0/1 [up/up] FE80::201:63FF:FEB0:B802 2001:DB8:0:1:201:63FF:FEB0:B802 GigabitEthernet0/2 [administratively down/down] unassigned Vlan1 [administratively down/down] unassigned
The ipv6 address matches our answer.
PC1’s default gateway should be 2001:DB8::230:F2FF:FE36:4502, and2001:DB8::2/64
PC2’s default gateway should be 2001:DB8:0:1:201:63FF:FEB0:B802.2001:DB8:0:1::2/64
3. Enable IPv6 on G0/0 of R1/R2 without explicitly configuring an IPv6 address. R1’s Configuration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 R1(config)#int g0/0 R1(config-if)#ipv6 enable R1(config-if)# R1(config-if)# R1(config-if)#do show ipv6 int brief GigabitEthernet0/0 [up/up] FE80::230:F2FF:FE36:4501 GigabitEthernet0/1 [up/up] FE80::230:F2FF:FE36:4502 2001:DB8::230:F2FF:FE36:4502 GigabitEthernet0/2 [administratively down/down] unassigned Vlan1 [administratively down/down]
This enables a link-local address: FE80::230:F2FF:FE36:4501. Notice that the link-local address for g0/0 is different from g0/1. This is because interfaces have different MAC addresses.
R2’s COnfiguration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 R2(config-if)#do show ipv6 int brief GigabitEthernet0/0 [up/up] FE80::201:63FF:FEB0:B801 GigabitEthernet0/1 [up/up] FE80::201:63FF:FEB0:B802 2001:DB8:0:1:201:63FF:FEB0:B802 GigabitEthernet0/2 [administratively down/down] unassigned Vlan1 [administratively down/down]
A link-local address is configured: FE80::201:63FF:FEB0:B801.
R1’s Static Route to R2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 R1(config)#ipv6 route ? X:X:X:X::X/<0-128> IPv6 prefix R1(config)#ipv6 route 2001:db8:0:1::/64 ? Dialer Dialer interface Ethernet IEEE 802.3 FastEthernet FastEthernet IEEE 802.3 GigabitEthernet GigabitEthernet IEEE 802.3z Loopback Loopback interface Serial Serial Vlan Catalyst Vlans X:X:X:X::X IPv6 address of next-hop R1(config)#ipv6 route 2001:db8:0:1::/64 g0/0 FE80::201:63FF:FEB0:B801
We can make use of the link-local addresses we generated for R1 and R2’s g0/0 interfaces.
The command is ipv6 route exit-int ipv6 address.
R2’s Static Route Configuration to R1 1 2 3 R2(config)# R2(config)#ipv6 route 2001:db8::/64 g0/0 FE80::230:F2FF:FE36:4501 R2(config)#
Check if configurations work by pinging PC2 from PC1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 C:\>ping 2001:db8:0:1::2 Pinging 2001:db8:0:1::2 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 2001:DB8:0:1::2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=126 Reply from 2001:DB8:0:1::2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=126 Reply from 2001:DB8:0:1::2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126 Reply from 2001:DB8:0:1::2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=126 Ping statistics for 2001:DB8:0:1::2: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms