Overview
- What is a LAN?
- Broadcast domains
- What is a VLAN?
- What is the purpose of VLANs?
- How to configure VLANs on Cisco switches?
What is a LAN?
A LAN is a single broadcast domain, including all devices in that broadcast domain.
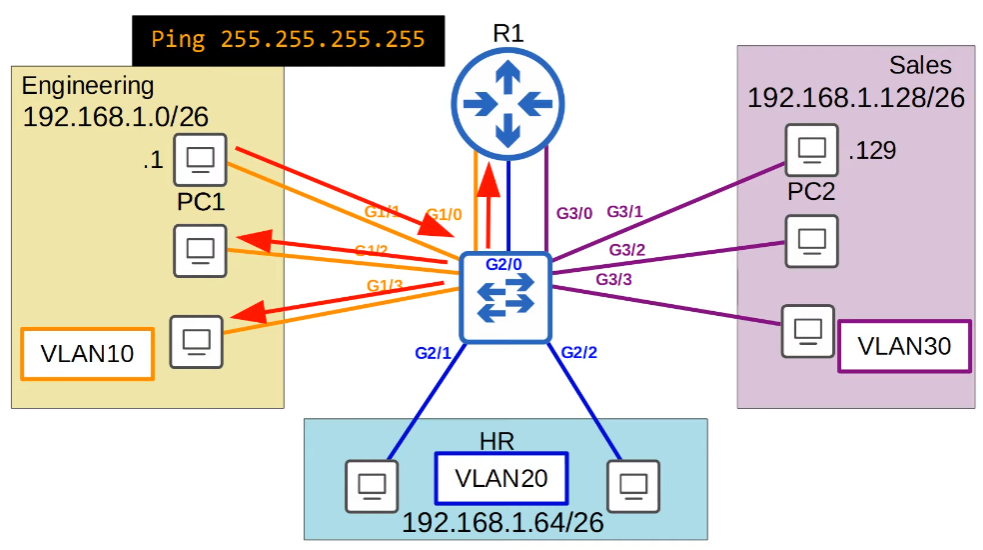
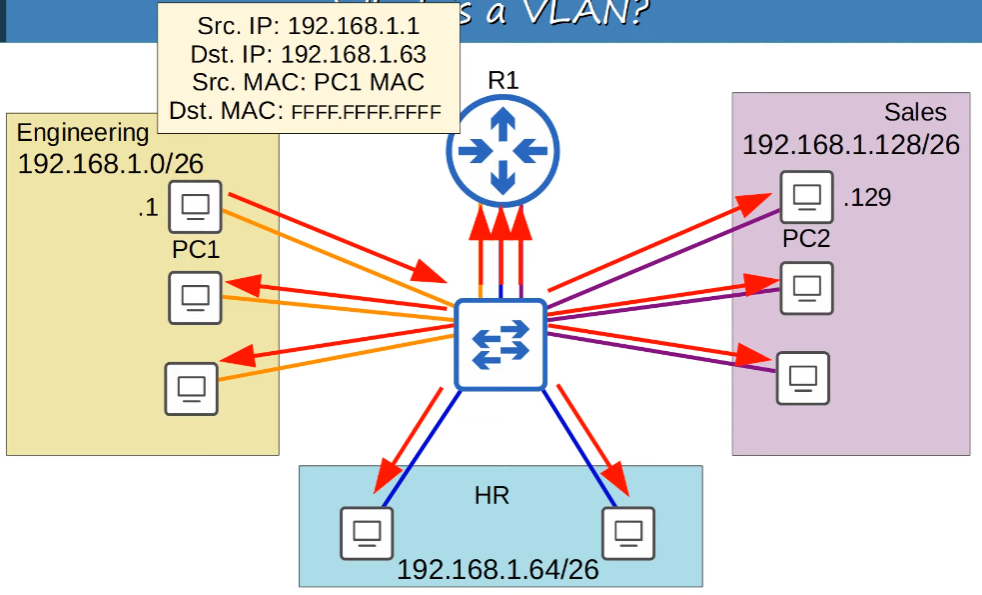
A broadcast domain is the group of devices which will receive a broadcast frame (destination MAC FFFF.FFFF.FFFF) sent by any one of the members.
When a switch receives a broadcast frame, it’ll flood the network.
Routers will simply drop broadcast frames.
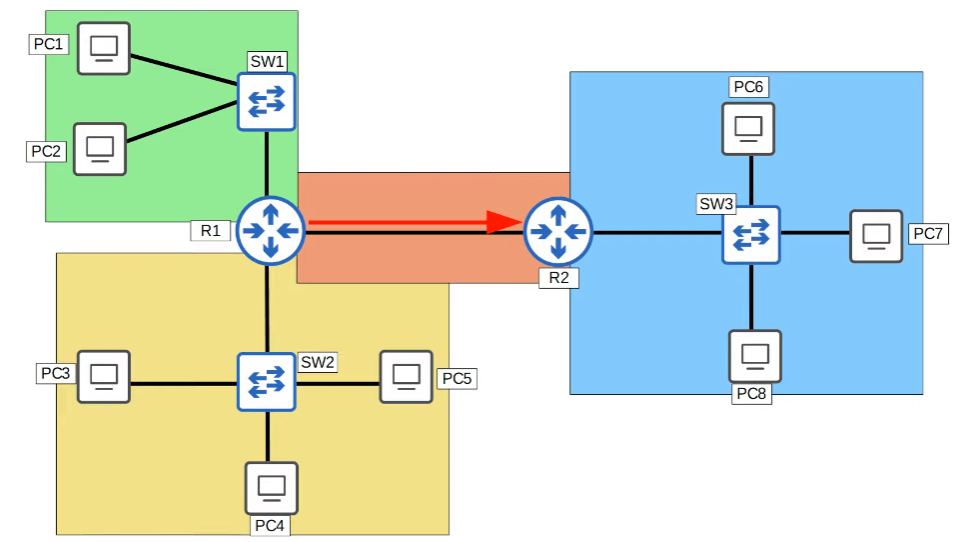
What is a VLAN?
The following image shows one network. The issue with the image is that if one department sends a broadcast frame intended for itself, the switch will flood everyone.
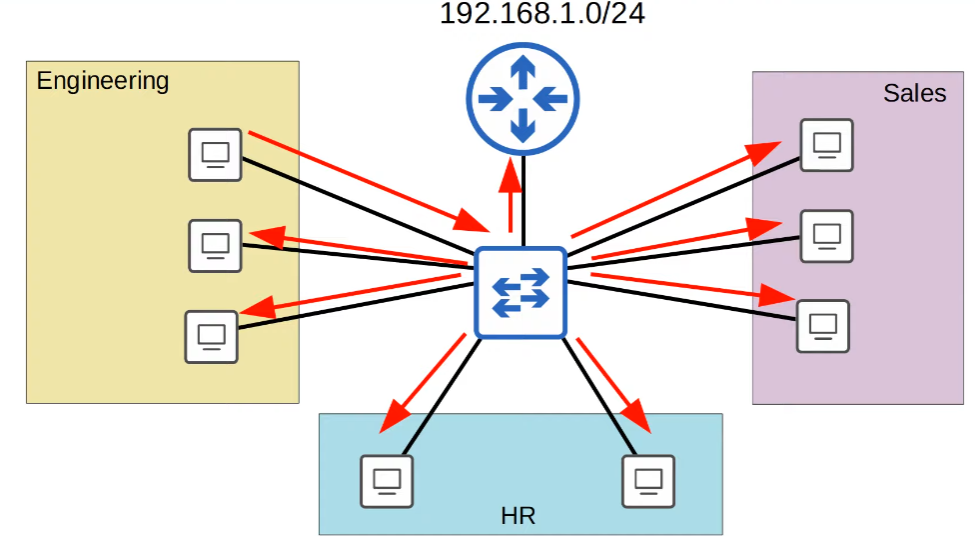
Performance: Lots of unnecessary broadcast traffic can reduce network performance.
Security: Even within the same office, you want to limit who has access to what. You can apply security policies on a router/firewall.
- Because this is one LAN, PCs can reach other other directly, without traffic passing through the router. So even if you configure security policies, they will not be effective.
We can separate these departments into their own subnets. Each subnet requiring a separate interface to the router. Information destined from one department to another will be directed to the router (which decapsulates and encapsulates with its own MAC address) before being sent to another department (subnet).
Nevertheless, the issue remains that a switch is a layer 2 device. Therefore, it remains unaware of subnets and works based off layer 2 information such as MAC addresses. A broadcast address will still flood the network because every device is still within the broadcast domain.
A possible solution is to buy a separate switch for each department. This could be expensive.
Another solution is a VLAN.
- Each department gets their own VLAN, which can be configured on the switch interfaces.
- VLANs are connected by their interfaces.
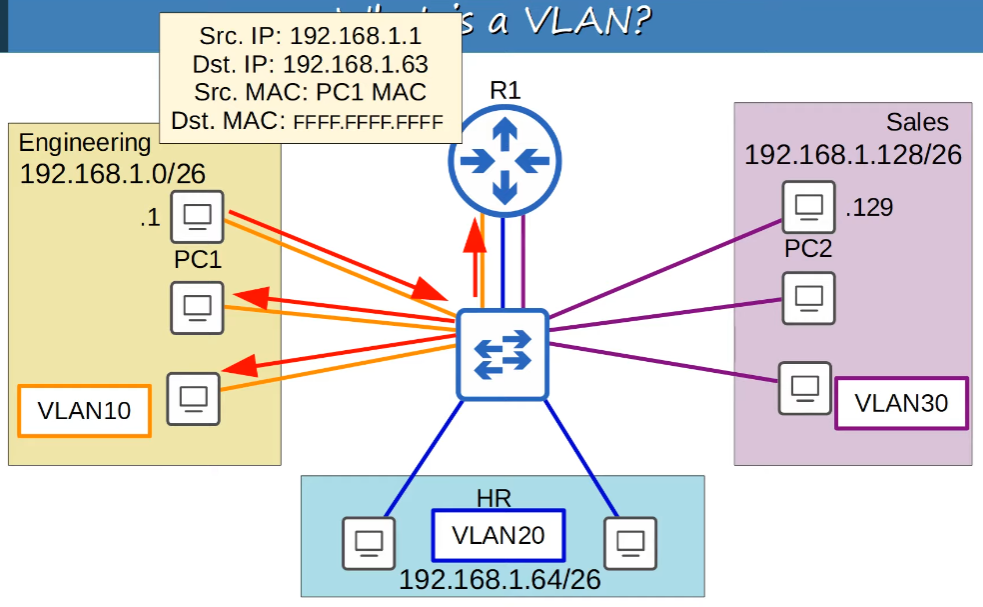
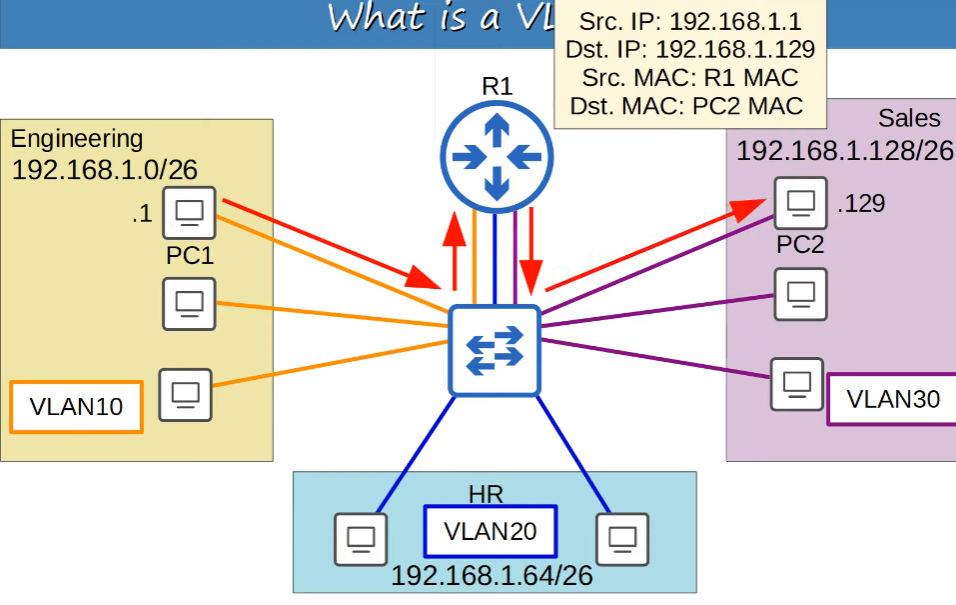
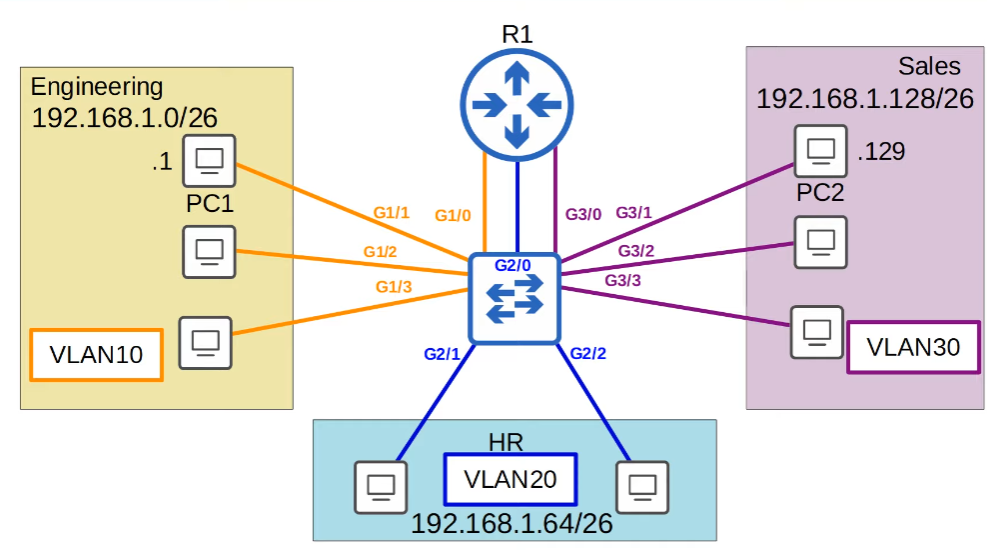
VLANs are configured on switches on a per-inferface basis.
VLANs logically seperate end hosts at Layer 2.
Switches do not forward traffic directly between hosts n different VLANs.
VLAN Configuration
Cisco CLI VLAN Configuration
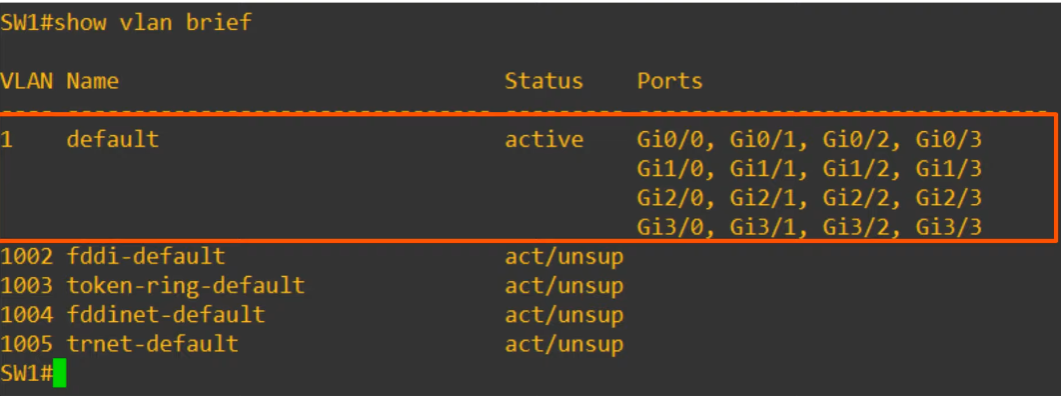
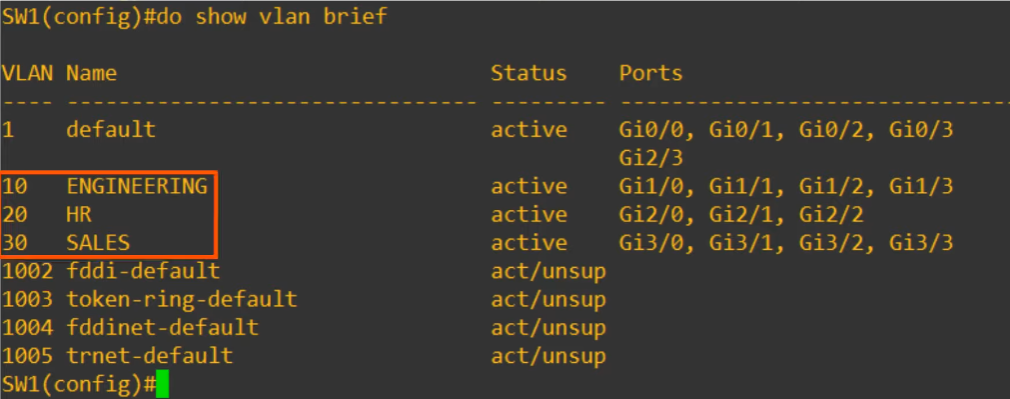
- VLAN 1, 1002,1003,1004,1005 exist by default and CANNOT be deleted.
Assign interfaces to a VLAN
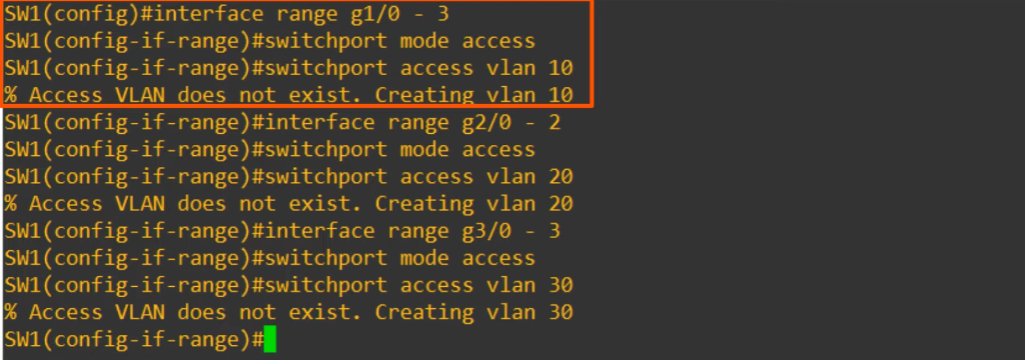
interface range g1/0 -3- accessing multiple interfaces at once
switchport mode access- an access port is a switchport which belongs to a single VLAN, and usually connects to end hosts like PCs. (access port because it gives the end host -access- to the network)
- Switchports which carry multiple VLANs are called trunk ports
- A switchport connected to an end host should enter “access mode” by default. However, it’s always better to explicitly configure the setting.
switchport access vlan 10- Command that assigns the VLAN to the port.
- VLAN10 is automatically created if it doesn’t exist.
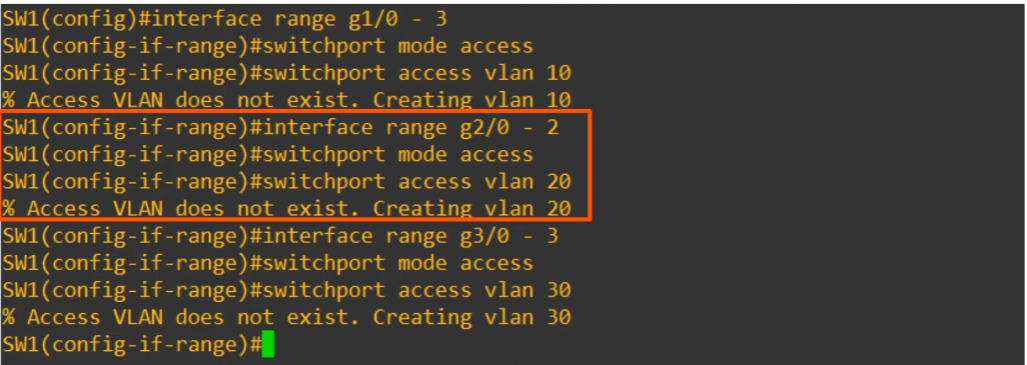
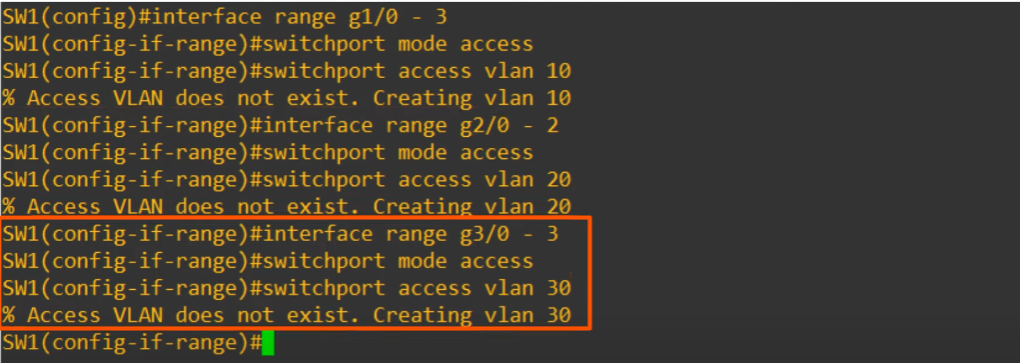
- Three separate VLANs were created.
Configuring VLAN names
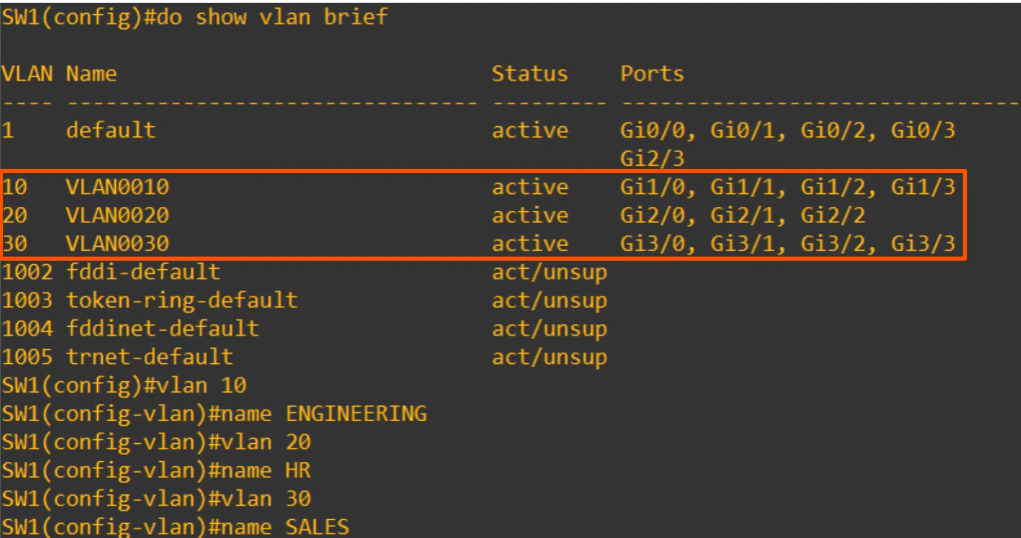
vlan 10; creates a VLAN (and also selects the VLAN)name ENGINEERING; sets the name
What if we broadcast via PC1?