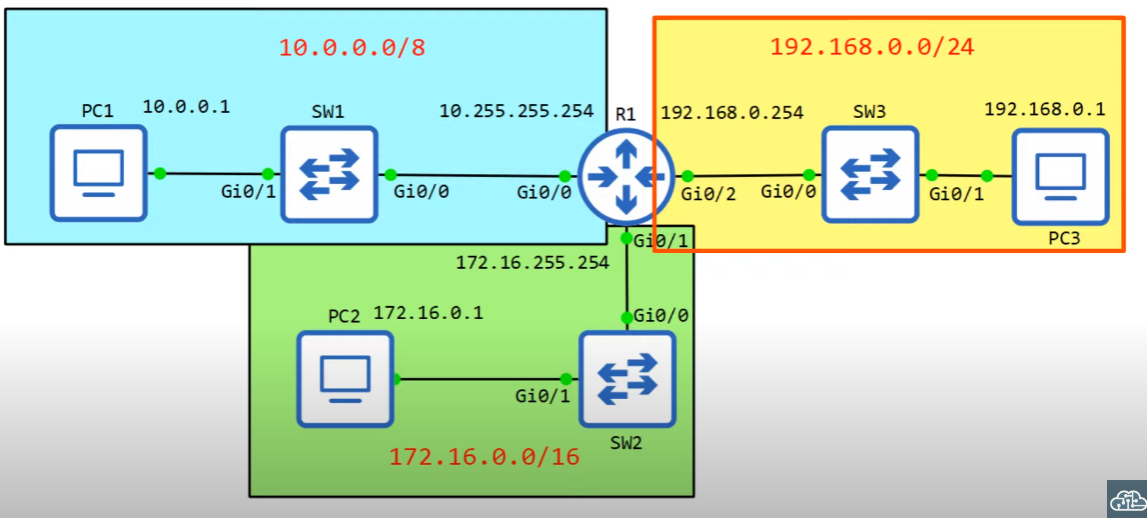
Overview
- IPv4 Address Classes (review and clarification)
- Finding the: maximum number of hosts, network address, broadcast addsress, firstusable address, last usable address (on a particular network)
- Configuring IP addresses on Cisco Devices
| Class | First octet | First octet numeric range | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0xxxxxxx | 0-127 | Usable range is 1 - 126 | |
| B | 10xxxxxx | 128 - 191 | ||
| C | 110xxxxx | 192-223 | ||
| D | 1110xxxx | 224-239 | Reserved for multicast (different from unicast and broadcast) | |
| E | 1111xxxx | 240-255 | Reserved for experimental use |
Calculate Maximum Hosts Per Network
Class C
192.168.1.0/24 -> 192.168.1.255/24
- Host portion = 8 bits = 2^8 = 256
- 192.168.1.0/24 = network address
- 192.168.1.255/24 = broadcast address
- 256 - 2 = 254
Class B
172.16.0.0/16 -> 172.16.255.255/16
- Host portion = 16 bits = 2^16 = 65,536
- 172.16.0.0/16 = network address
- 172.16.255.255/16 = broadcast address
- Maximum hosts per network = 65,534
Class A
10.0.0.0/8 -> 10.255.255.255/8
- Host portion = 24 = 2^24 = 16,777,216
- 10.0.0.0/8 = network address
- 10.255.255.255/8 = broadcast address
- Maximum hosts per network = 16,777,214
Maximum host per network = 2^n - 2
First/Last Usable Address
Class C
192.168.1.0/24 -> 192.168.1.255/24
- First usable address = 192.168.1.1/24
- Last usable address = 192.168.1.254/24
Class B
172.16.0.0/16 -> 172.16.255.255/16
- First usable address = 172.16.0.1/16
- Last usable address = 172.16.255.254/16
Class A
10.0.0.0/8 -> 10.255.255.255/8
- First usable address = 10.0.0.1/8
- Last usable address = 10.255.255.254/8
Configuring Cisco Router with IP Address
Create the following configuration using Cisco.
Log in to CLI of R1
1 | R1>en |
- Status: refers to Layer 1 status
- Protocol: Layer 2 status
Now to edit the interface – do the following in global configuration mode
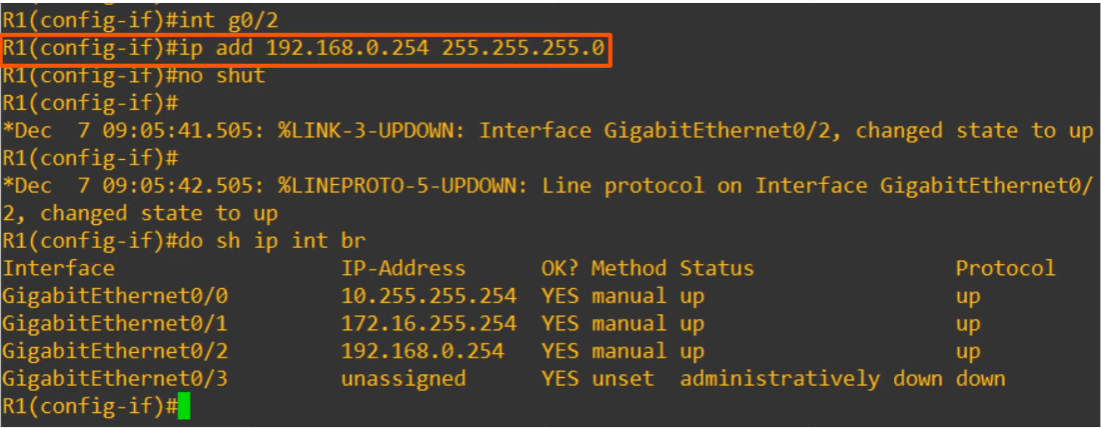
Now that we are inside the ethernet config, we can assign an IP address to that specific interface.
Notice that we must type out the Cisco netmask (and not the slash notation) for this class A network.
Also recall that Cisco router interfaces have the “shutdown command” applied to them by default. We disabled that command with
no shutdown.
dois used to execute a privileged EXEC command from config mode.do sh ip int br=do show ip interface brief
The interface configuration is a success.
Let’s do the config for the Gi0/1 interface next.
We want the network address is 172.16.255.254 for the router…(?)
The network is 172.16.0.0/16. What will the subnet mask be?
We can directly switch from one interface to another. Notice how we left off at the previous int g0/0. Now we are in
int g0/1
Let’s configure R1 Gi0/2 interface to have an ip address of 192.168.0.254.
- Given the prefix is /24. The subnet mask should be 255.255.255.0.
Other show commands
#show interface: will show way too many interfaces. so it’s important to be specific.- specify the interface.
- GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up.
- GigabitEthernet0/0 is up : layer 1 is working.
- line protocol is up : refers to layer 2 status of the interface.
#show interfaces description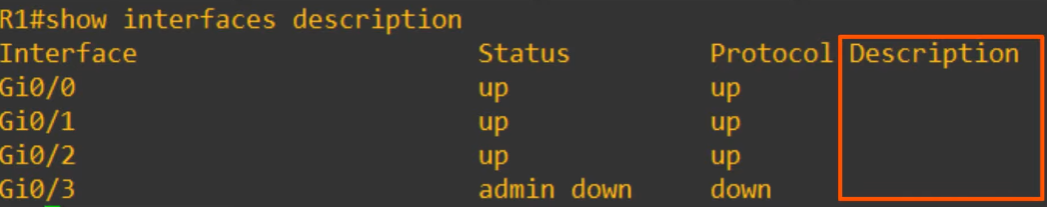
To configure a interface description: description LINE
