Recall Layer 3: Network Layer
- Provides connectivity between end hosts on different networks (outside of the LAN)
- Provides logical addressing (IP addresses)
- Provides path selection between source and destination.
- Routers operate at Layer 3
Routing
- Recall switches simply expand networks. Therefore, PCs within the same LAN have the same IP addresses within the same network.
What does the IP address indicate?
- The three group 192.168.X indicates network itself.
- Y in 192.168.X.Y represents the PCs/clients/servers.
- The
/24represents the network and which part represents the end-host./24says the first 3 group of the numbers represents the network.
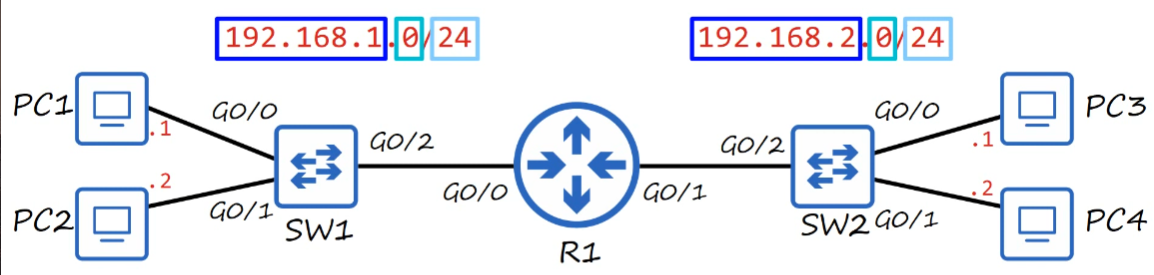
The router in the picture above requires an IP address.
G0/0interface is given 192.168.1.254G0/1interface is given 192.168.2.254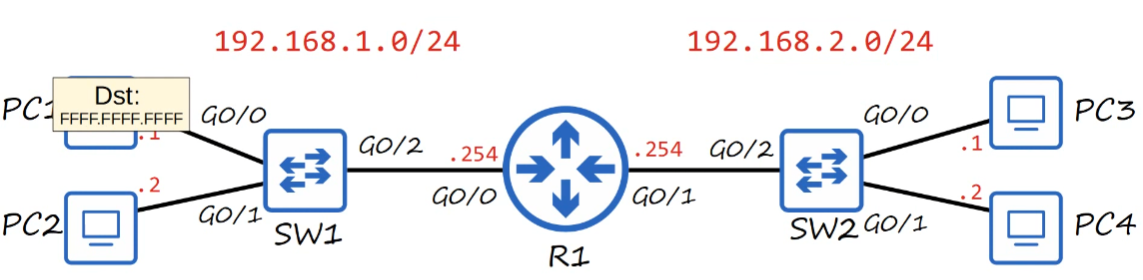
- The broadcast signal is forwarded to 192.168.1.2 and 192.168.1.254.
- Broadcast signals are limited within the local network.
IPv4 Header (Let’s focus on Source and Dest IP address atm)
- IP addresses are 32 bits (4 bytes) in length.

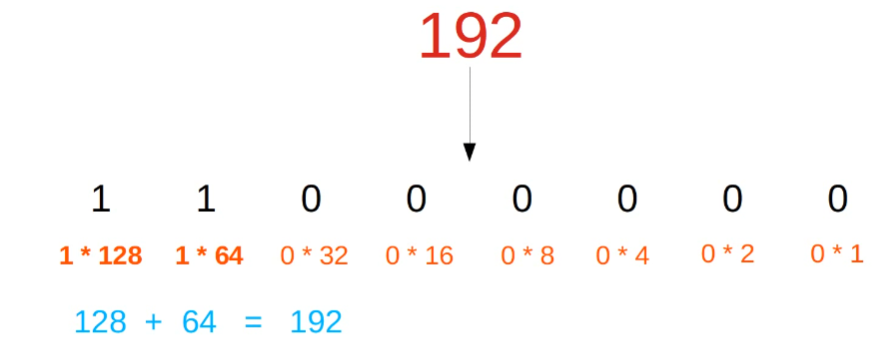
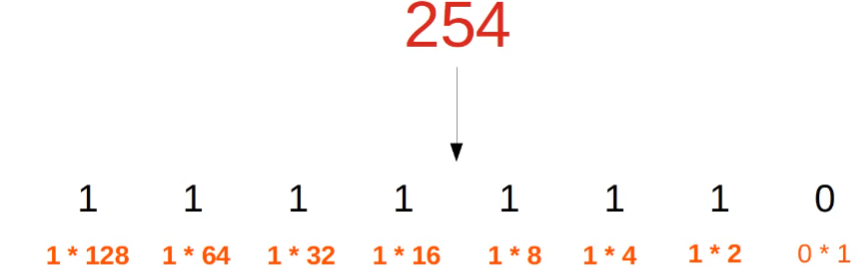
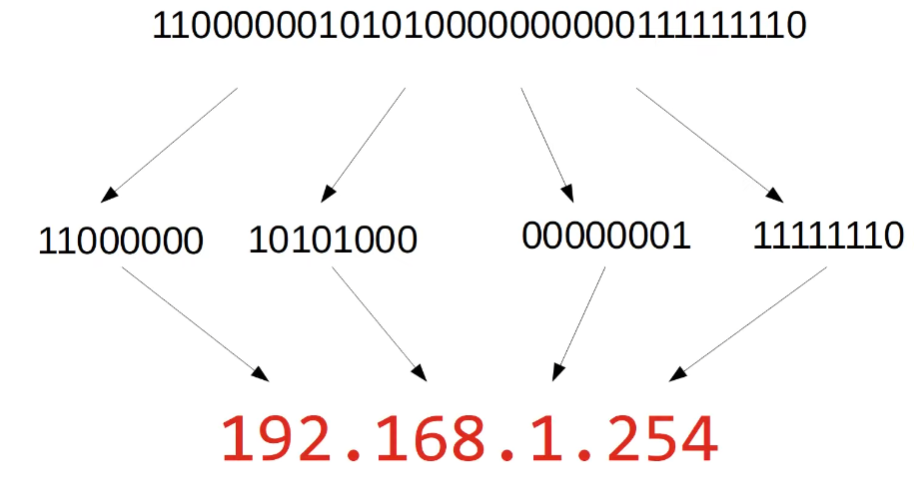
192.168.1.254: A closer look
- Each group of numbers represents 8 bits.
- 192 = 8 bits => 11000000
- 168 = 8 bits => 10101000
- 1 = 8 bits => 00000001
- 254 = 8 bits = 11111110
- Instead of binary, we use dotted decimal.
Recall Decimal, Hexadecimal, and Binary Notation
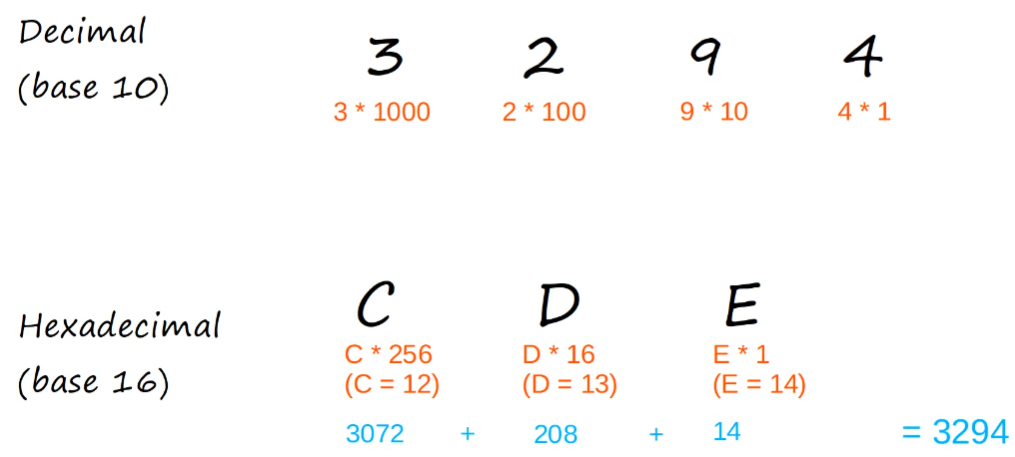
Decimal to Binary…

The range of possible numbers of binary can range from?
0 - 255
IPv4 address is a series of 32 bits
So what is the /24?
- The
/24indicates the first 24 bits represents the network portion, and the remaining 8 represents the host.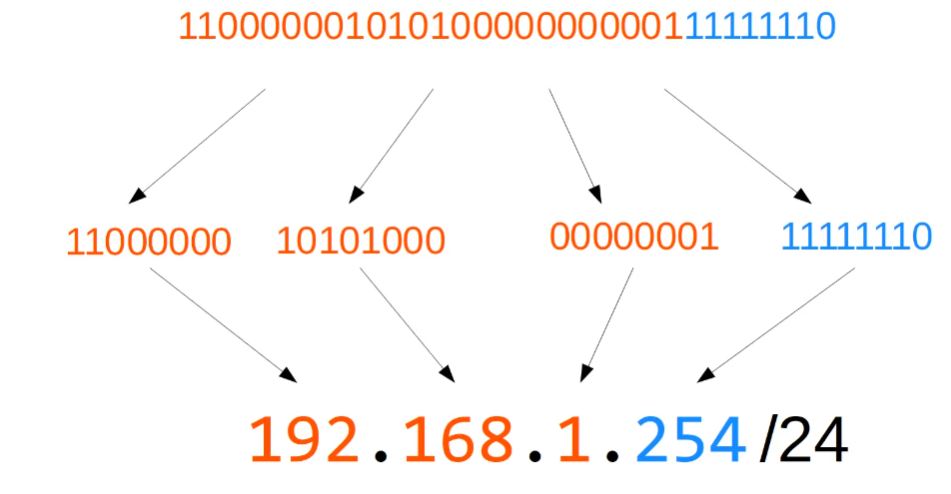
/16 indicates the first half.

/8

IPv4 Address Classes
| Class | First octet | First octet numeric range | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0xxxxxxx | 0-127 | 64+32+16+8+4+2+1 = 127 | Really 0 - 126, not 127. |
| B | 10xxxxxx | 128 - 191 | 128 + 32 + 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 191 | |
| C | 110xxxxx | 192-223 | ||
| D | 1110xxxx | 224-239 | Reserved for multicast (different from unicast and broadcast) | |
| E | 1111xxxx | 240-255 | Reserved for experimental use |
Why is class A range in practice only 0 - 126? Loopback Addresses
- The 127 octet range is reserved for loopback addresses. What does that mean?
- The first octet is always 127.
- Address range 127.0.0.0 - 127.255.255.255
- Used to test the ‘network stack’ (think OSI, TCP/IP model) on the local device.
- If a device sends any network traffic in this range, it’s simply sent back up the network stack (think of when you receive a packet and it’s being de-encapsulated).
- This is demonstrated by the RTT when pinged.
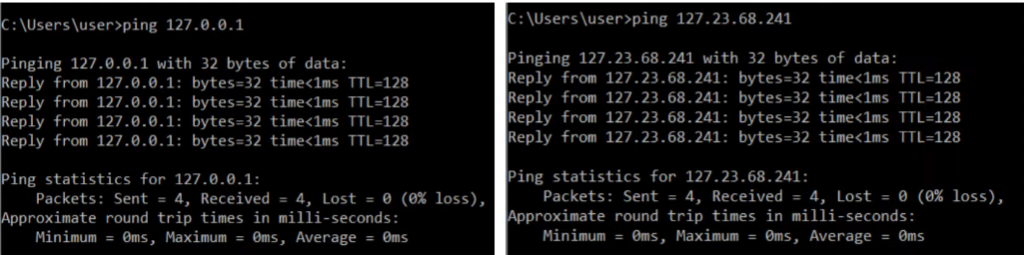
- The first octet is always 127.
Implications of Class A, B, C.
| Class | First octet | First octet numeric range | Prefix Length | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0xxxxxxx | 0-127 * really 0 - 126 | /8 | ||
| B | 10xxxxxx | 128 - 191 | /16 | ||
| C | 110xxxxx | 192-223 | /24 |

- Class A: Fewer potential networks, there can be many hosts on each network
Class C: there are many possible networks, but there can only be a few hosts.
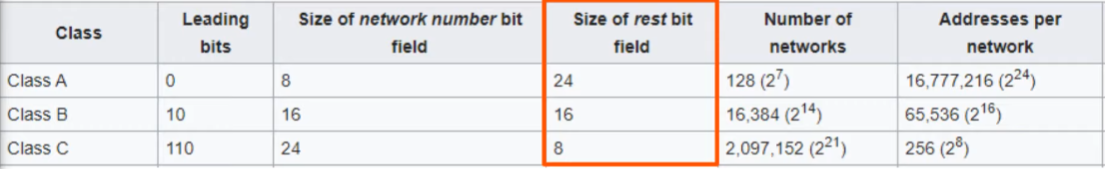
- Indicated by the chart above, class C networks can only have 256 possible hosts.
- However, the first bit is reserved for the network. AND the last address of the network is the broadcast network (the layer 3 address when you want to send traffic to all host
- So really, the host count is 2 LESS. 256 - 2 = 254 in class C
Netmask: “A Newer and Easier Way of Writing the Prefix Length?”
In juniper networks, we use the slash notation.
- Class A: /8
- Class B: /16
- Class C: /24
Cisco networks use an older method: dotted decimal netmask
- Class A: 255.0.0.0 (11111111 00000000 00000000 00000000)
- Class B: 255.255.0.0 (11111111 11111111 00000000 00000000)
- Class C: 255.255.255.0 (11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000)
The network address CANNOT be assigned to the host.
- If the host portion of the address is all 0’s, then it is a network address.
192.168.1.0/24 = network address
192.168.2.0/24 = network address
The first usable host address is 192.168.1.1/24
The last address in the network is the broadcast address.
- If the host portion of the address is all 1’s, then it is the broadcast address.
192.168.1.255/24 (X.X.X.1111111)
The last usable host address is 192.168.1.254/24
In short, we talk about
- Dotted decimal and binary
- Network portion / host portion of IPv4
- IPv4 address classes
- Prefix lengths / netmasks (Cisco)
- Network address / broadcast address
Question 0
If we sent a ping to 192.168.1.255, what would be the destination MAC address?
- Given that 255 is the broadcast address, the destination MAC address should be FFFF.FFFF.FFFF